Arduino Simple Serial communication with multiple values
Sending values from an Arduino to a computer can sometimes be a bit daunting... Sending only one value is pretty straightforward, but when it comes to sending multiple values, there are many scenario's on how to send out the values in a manner that enables you to distinguish them properly on the computer side.
This page offers an explanation and the example code to prepare for this task in a simple, straightforward way.
Arduino communicates to other devices over USB (User Serial Bus) this means that, by default, everything that is sent out is Serialised: the communication contains only one message at a time, bigger messages or chunks of data will be split into pieces that are sent one at a time, after each other.
(as opposed to Parallel communication, where multiple messages are sent and transfer, parallel to each other, at the same time)
Before we can get to sending out any values, we first have to initialise Serial communication from the Arduino by putting the following command in void setup()
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //start Serial communication with a speed of 9600 baud
}Serial communication has a significant draw on both the computing power of the Arduino microcontroller ánd power consumption, that's why the Serial port on the board is off by default.
Now we're ready to start sending data!
So, when you want to send out values from, lets say, all Analog outputs, you can send out all the values one by one, using a for loop in void loop() like this:
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { //iterate through all the analog inputs
int value = analogRead(i); //put the read value into and int variable
Serial.print(value); //and send the value out over Serial
}
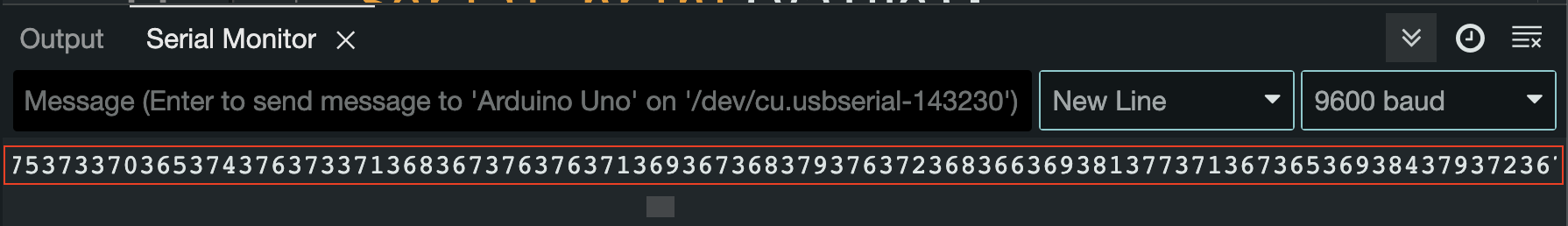
Let's test this on Arduino and have a look at the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE to see what kind of data is coming in..
When sending the data out this way, all the incoming values are concatenated together in one big chunk of numbers... There's no way of distinguishing the separate analog values anymore.
The serial monitor is reading values in one row until it encounters a 'newline' character ('\n') since we never send a 'newline', all the numbers are read in one long oblivious stream.
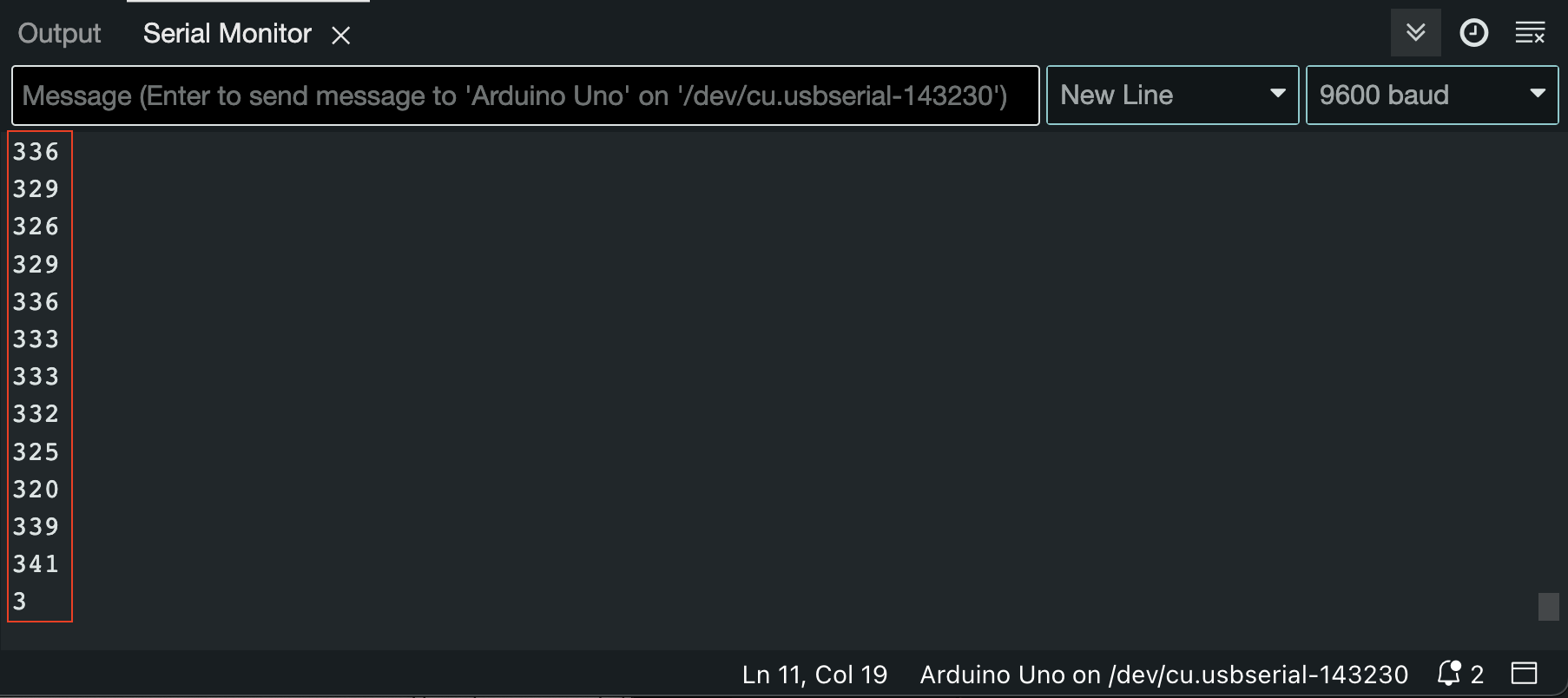
We could easily fix this by changing the Serial.print(value); line to Serial.println(value);, The Serial.println() command, forces the Arduino to send a 'newline' after each value, resulting in the values coming in into the console like this:
Now, at least all the different input values are shown separately, but now there's no way of distinguishing which number belongs to which input...!